Efficiency has always been the king. But how do companies crack it down so seamlessly? This is when business process management (BPM)— the secret to many successful organizations—comes into the picture!
According to Research Gate, business process management or BPM empowers businesses to target realizable business value and eventually allows them to point digital initiatives for companies on those targets.
In simpler words, it is like a well-oiled machine that can both improve efficiency and cut down costs—that is exactly the power of BPM.
So, be it a startup or a well-established company, understanding and implementing BPM is a must. This blog discusses everything about business process management, right from its meaning to some must-know best practices. Let’s dive in.
What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
Business process management (BPM) is the disciplined approach to make an organization’s workflow effective, efficient, and agile. In simpler words, it is the analysis, design, implementation, monitoring, and continuous improvement of business processes.
Say, for instance, consider a customer service department:
- A customer complains (input)
- The complaint is then recorded and filed
- It is then assigned to the right team
- The team checks & addresses the challenge
- The resolution is communicated to the customer (output)
BPM would optimize the whole process, maybe by automating steps, setting performance metrics, or even redesigning the workflow to reduce response time. Logically, BPM helps fine-tune the operations of organizations to achieve better results with less waste.

Why is BPM Important?
By implementing business process management, you can:
- Eliminate redundancies, reduce costs, and manage operations better. An IDC survey suggests that companies implementing BPM solutions saw an average cost reduction of 20 percent.
- Standardize procedures to increase quality and reduce errors
- Increased customer satisfaction—faster and uniform service
- Increase agility to act faster on changes in the market
- According to AIMultiple, BPM Boost productivity and satisfaction of employees by defining clear roles and responsibilities
- Comply with regulations and industry standards
- Make better decisions through real-time process insights
- Spot areas for improvement to foster innovation
- Improve collaboration across departments
- Handle scaling operations more effectively as your business grows
There is no denying that business process management leads to exponential growth in the longer run.

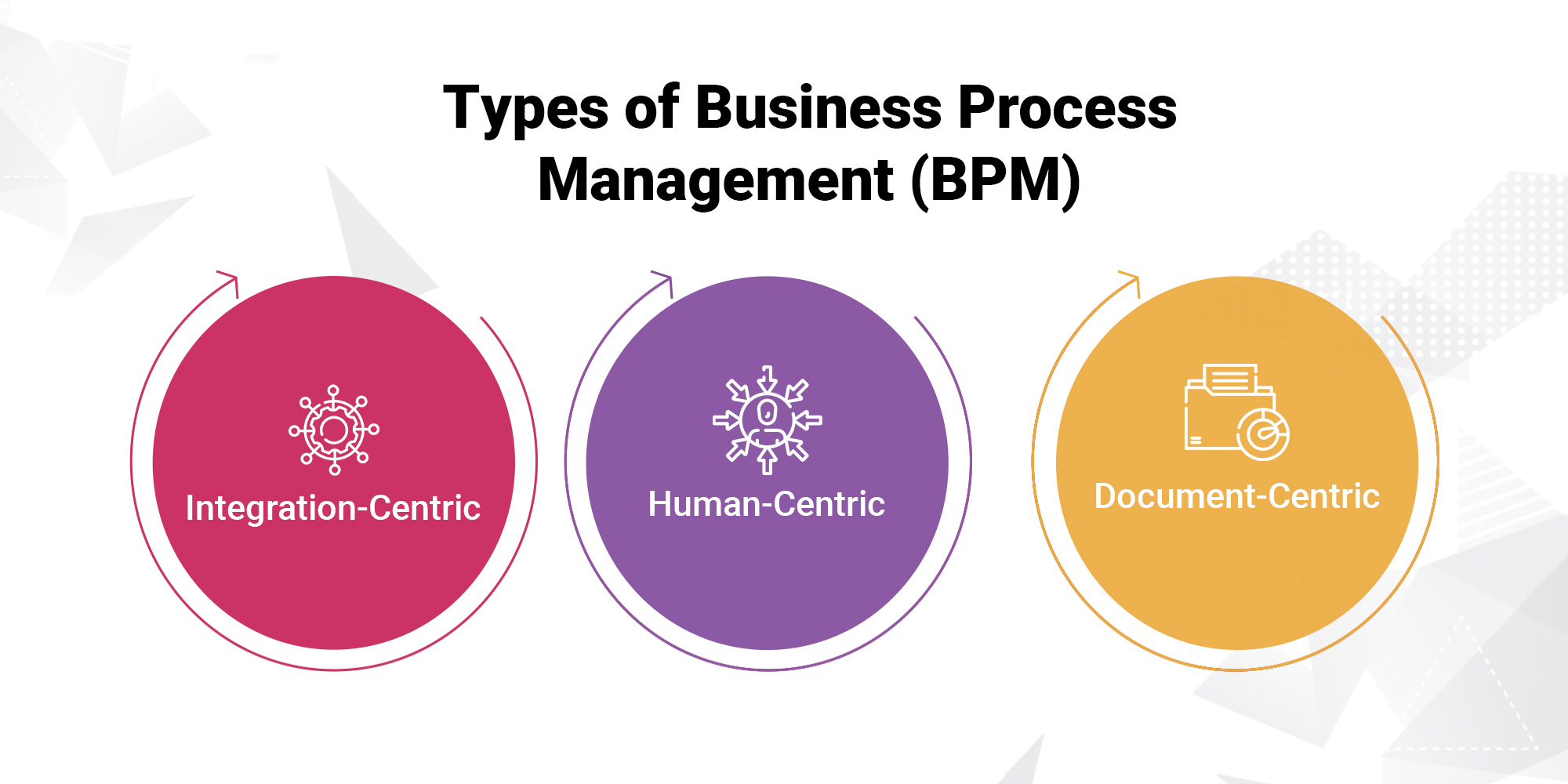
Types of BPM
Take a look at the top three types of business process management:
1. Integration-Centric BPM
As the name suggests, this type involves integration between different systems and applications of an organization. It facilitates transfer of data between applications and execution of business processes, avoiding manual work and potential errors. In other words, this will be ideal for organizations that have critical IT infrastructures and would help in increasing efficiency by interlinking CRM and ERP systems.
2. Human-Centric BPM
This is a people-centric approach to process management. It presents easy user interface facilities, and provides tools to manage tasks correctly, which is conducive to making the right decisions and collaboration. Since it’s not feasible to fully automate every process, it makes staff capable of efficiently handling complex situations with the knowledge and tools necessary for the most appropriate action.
3. Document-Centric BPM
This management type controls the document flow around the organization. This is very important in industries that have huge transactions in documents. It digitizes, organizes, and tracks paperwork. Technologies like OCR and electronic signatures make document-based processes easier, hence improving efficiency and compliance with retention policies.
5 Ways to Adjust Your CX as per consumer behaviour
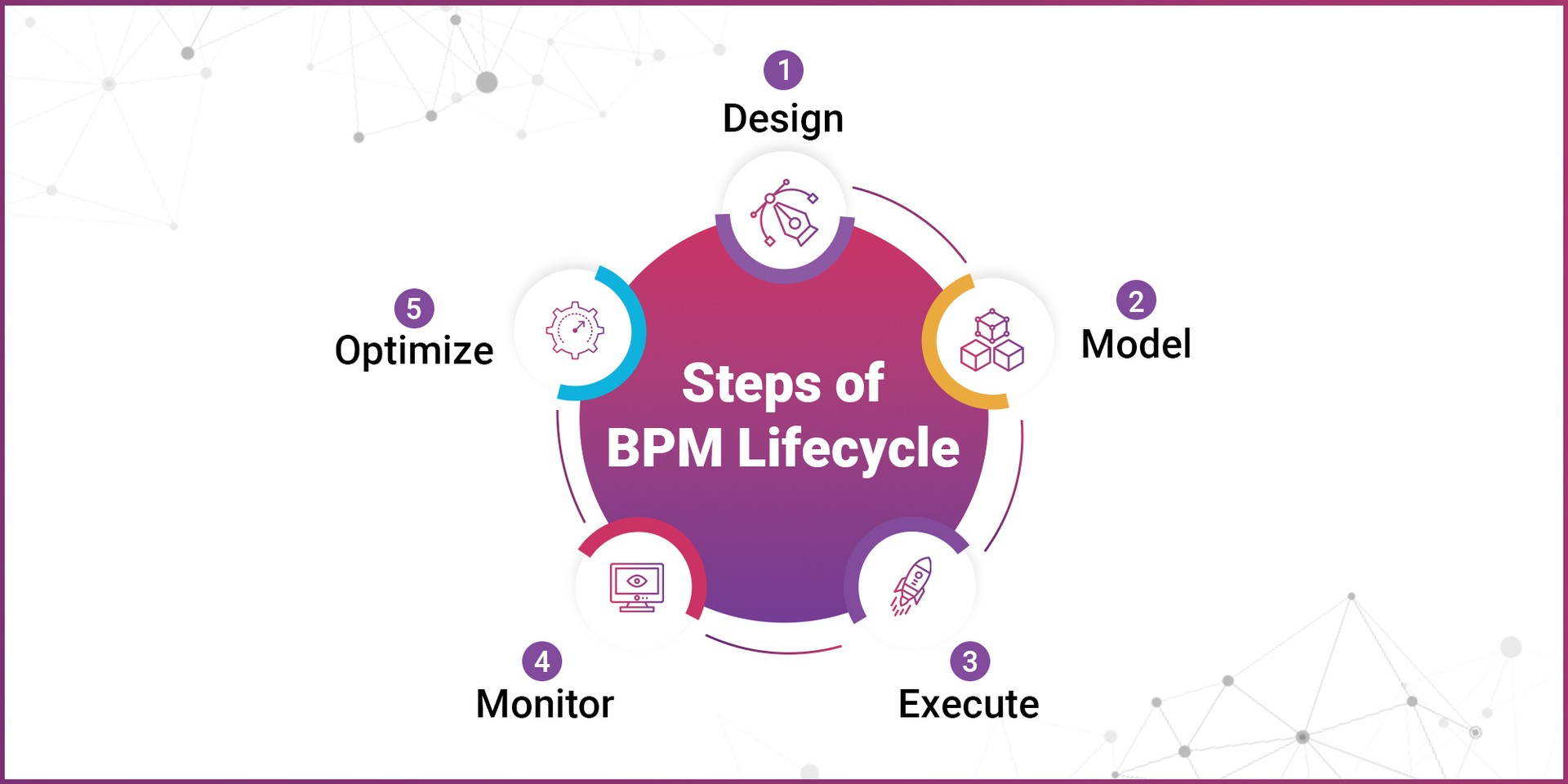
Steps of BPM Lifecycle
Here are the five vital steps in business process management you must be aware of:
1. Design
This first step consists of identification and mapping of existing processes. Business analysts and stakeholders work together to understand the current workflows, to describe the goals and delineate how the process ought to appear in an ideal situation. They identify process boundaries, inputs, and outputs, including identifying KPIs for the process.
The design phase lays the groundwork and articulates the objectives of the entire process.
2. Model
In this step, the designed process is turned into a visual or some kind of simulation. Using different tools, detailed flowcharts or diagrams of each step, decision point, and data flow are created by the teams. This model further enables the stakeholders to see what the process looks like, think through probable bottlenecks, and run various scenarios before it actually gets implemented.
3. Execute
Execution means that the modeled process has to be implemented in real-world operations. This could involve deploying new software, training employees, and integrating the process with existing systems.
Most importantly, attention should be paid to the smoothness of the transition and least possible disruption of ongoing business activities. Proper execution will ensure theoretical improvements translate into practical benefits.
4. Monitor
Once live, the process is monitored. This step involves data collection in terms of process performance and tracking of KPIs regarding deviations from the expected outcomes. Monitoring tools allow for real-time insights related to process efficiency, bottlenecks, and attention areas.
This step is very important in keeping the process effective and assuring improvement opportunities.
5. Optimize
The monitored data is examined in this step, and improvement areas are identified. This information is then used by teams to take data-driven decisions on the process modifications. Some examples of the changes could involve removal of redundant steps, automation of manual tasks, and reallocation of resources.
This step ensures that the process will keep evolving and improving along the way and stay relevant to the business goals.
5 Best Practices in Business Process Management
Now that you know almost everything about business process management, it is now time to explore some best practices while implement:
1. Align With Business Strategy
Align all of your BPM initiatives with the overall goals and strategies of your organization. It allows process prioritization for improvement and ensures that your BPM efforts will lead to organizational success.
Also, it is equally important to regularly review and adjust processes to ensure it is relevant to your business needs.
2. Involve Stakeholders
Engage all employees from the front line to top management in the BPM process. Their insights are crucial to spot inefficiencies and possible improvements. Cultivate a culture where each employee feels empowered to suggest changes in processes for improvement, thus facilitating continuous improvement process.
3. Start Small and Scale
Start with a few or pay attention to enhance one process at a time. This way, you can demonstrate some quick wins, learn from the experience, and refine your BPM methodology before taking on larger and more complex processes. Scale up gradually as you build up expertise and confidence.
4. Leverage Technology Wisely
Implement tools that are correct for your organization’s needs and capabilities. Choose flexible, simple-to-use solutions that integrate with other existing systems. Keep in mind that all technologies are only an enabler, not a solution in itself. So, first focus on improving your processes, and then identify technology to enable this.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Implement a mechanism for continuous monitoring and evaluation of processes. Monitor performance using metrics and KPIs in areas that signal possible improvements. Plus, design a feedback loop, providing an avenue for quick adjustments, and thus promoting continuous optimization. Do not forget that BPM is not a one-time project but a commitment to excellence.
Bottom Line
Business Process Management is not a tool; it is a way of mindset that can indeed revolutionize your organization. As we have learned, BPM provides the systematic means to automate, increase efficiency, and boost innovation capacity.
So, can your company afford to turn a blind eye to that competitive edge that BPM brings?
While facing the challenges of tomorrow, ask yourself: Will you be the one who disrupts or the one who is being disrupted? Embrace BPM and ensure that you’re not merely surviving but thriving in this age of digital transformation. Your future success may depend on it.